CYBER INSURANCE’S “PERFECT STORM
Cyber is a relatively new, evolving risk. Insurers manage their exposures, in part, by setting coverage limits and excluding events they don’t want to insure.
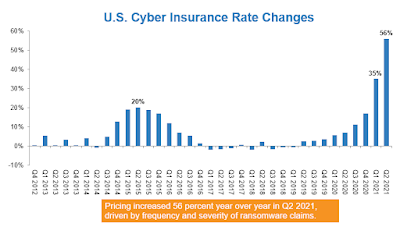
Increasing cybercrime incidents resulting in large losses – combined with some carriers retreating from writing the coverage – is driving cyber insurance premiums sharply higher.
Once a diversifying secondary line and another endorsement on a policy, cyber has become a primary component of any corporation’s risk-management and insurance-buying decisions. As a result, insurers need to review their appetite for the peril, risk controls, modeling, stress testing and pricing.
According to A.M. Best, the prospects for the cyber insurance market are “grim” for several reasons:
Rapid growth in exposure without adequate risk controls,
Growing sophistication of cyber criminals, and
The cascading effects of cyber risks and a lack of geographic or commercial boundaries.
Increasing cybercrime incidents resulting in large losses – combined with some carriers retreating from writing the coverage – is driving cyber insurance premiums sharply higher.
Once a diversifying secondary line and another endorsement on a policy, cyber has become a primary component of any corporation’s risk-management and insurance-buying decisions. As a result, insurers need to review their appetite for the peril, risk controls, modeling, stress testing and pricing.
According to A.M. Best, the prospects for the cyber insurance market are “grim” for several reasons:
Rapid growth in exposure without adequate risk controls,
Growing sophistication of cyber criminals, and
The cascading effects of cyber risks and a lack of geographic or commercial boundaries.
While the industry is well capitalized, A.M. Best says individual insurers who venture into cyber without thoroughly understanding the market can put themselves in a vulnerable position.
The cyber insurance industriousness is suffering a perfect storm between far-reaching technology peril, increased regulations, increased lawless exercise, and carriers pulling back content, ” according to Joshua Motta,co-founder and CEO of Coalition, a San Francisco- predicated cyber insurance and security company. “ We ’ve seen multiplex carriers sublimit ransomware content, add coinsurance, or add repulses. ”
Worsening since the infection
A recent Willis Towers Watson study establish primary and redundant cyber renewals equaling award increases “ well into the double integers. ” One factor helping to drive these increases, Willis writes, is the abrupt shift toward remote work on potentially less- secure networks and accoutrements during the plague, which has made brotherhoods more vulnerable to phishing and hacking.
The average cost of a data breach rose day over day in 2021 from$3.86 million to$4.24 million, according to a recent report by IBM and the Ponemon Institute — the loftiest in the 17 days that this report has been published. Costs were loftiest in the United States, where the average cost of a data breach was$9.05 million, up from$8.64 million in 2020, driven by a complex ministerial chorography that can vary from state to state, especially for breach advert.
The top five sedulity for average total cost were
Health care
Financial
Pharmaceuticals
Technology
Energy
For the health care sector, the average total cost rose29.5 percent, from$7.13 million in 2020 to$9.23 million in 2021.
Since the outset of the date, cyber insurance rates have increased 7 percent for small businesses, according to AdvisorSmith Results. For modest and large businesses, AdvisorSmith said, those increases were this to 20 percent.
Insurers ’ takes
AIG last month said it's straining terms of its cyber insurance, noting that its own award prices are up nearly 40 percent widely, with the largest increase in North America.
“ We continue to precisely reduce cyber limits and are capturing tighter terms and conditions to address augmenting cyber loss trends, the rising hazard associated with ransomware and the systemic nature of cyber hazard generally, ” CEO Peter Zaffino said on a conference call with commentators.
In May, AXA said it would stop writing cyber procedures in France that repay patrons for gouging payments made to ransomware miscreants. In a ransomware attack, hackers use software to block access to the victim ’s own data and demand payment to repossess access.
The FBI warns against paying securities, but studies have shown that business leaders now pay a lot in the makeshift of getting their data back. An IBM review of 600U.S. business leaders pioneer that 70 percent had paid a security to repossess access to their business strings. Of the companies responding, nearly half have paid fresh than$, and 20 percent paid fresh than$.
Two advisories last space fromU.S. Treasury agencies – the Monetary Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN FinCEN) and the Office of Foreign Substance Control (OFAC OFAC) – indicated that companies paying safeguard or loosening like payments could be subject to republican penalties. These notices italicize businesses ’ need to consult with knowledgeable, recognized professionals long before an attack occurs and before making any payments.
More like terror than inundation
Cyber trouble is unlike torrent and fire, for which insurers have decades of data to help them verbatim measure and price programs. Cyber troubles are comparatively new and constantly evolving. The presence of virulent intent results in their having other in common with terrorism than with natural catastrophes.
Insurers and policyholders need to be spouses in relieving these threats through continuously refining data hygiene, sharing of intelligence, and clarity as to content and its limits.
















No comments:
Post a Comment